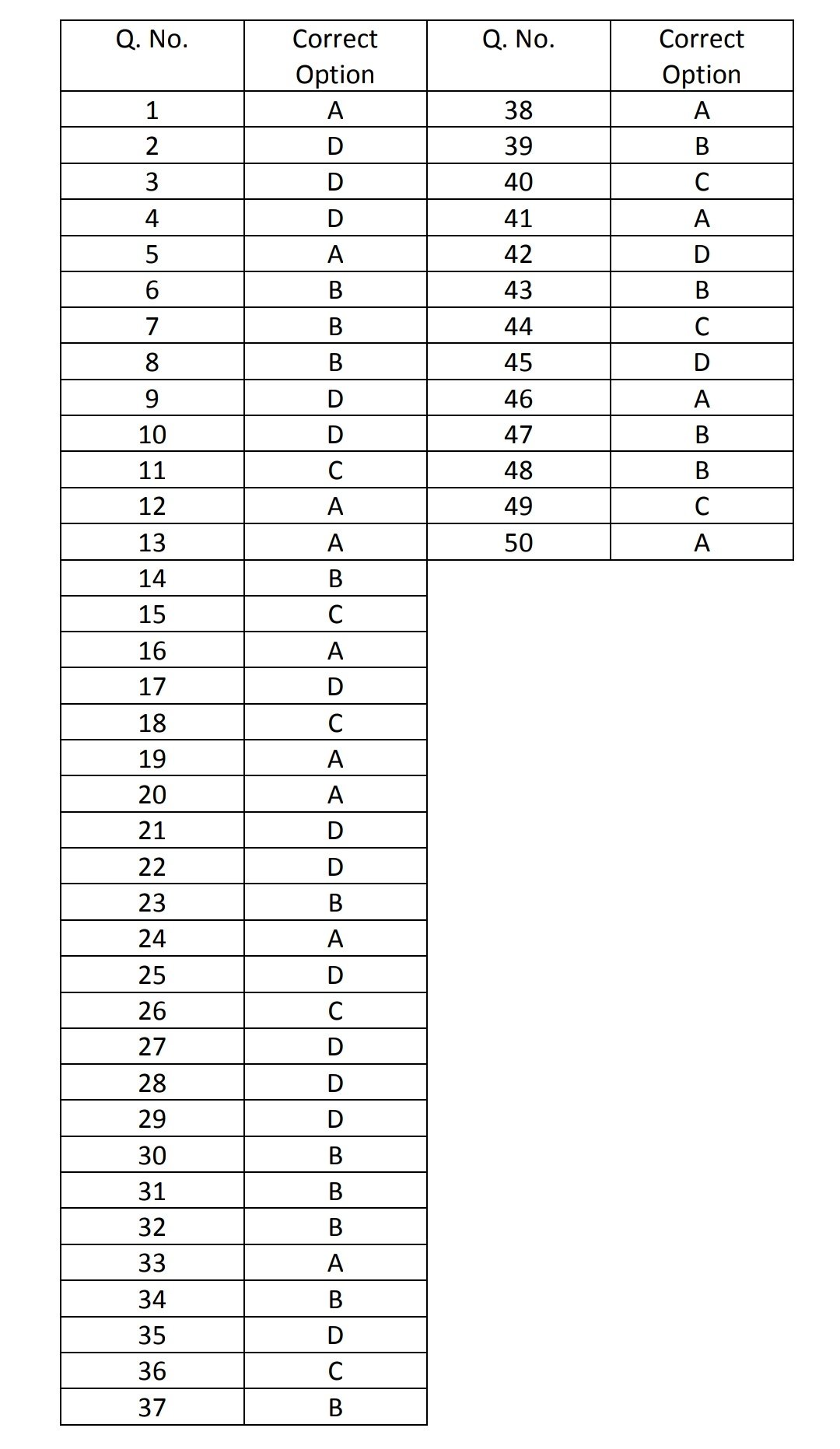
Pharmaceutics I
Practice Questions & Answer Key
1. Wool fat is also known as
A. Anhydrous lanolin
B. Lanolin
C. Petrolatum
D. Hydrous lanolin
2. Which of the following are Ointment bases
A. Oleaginous bases & Absorption bases
B. Absorption bases
C. Emulsion bases & Absorption bases
D. Oleaginous bases, Absorption bases & Emulsion bases
3. Petrolatum also termed as
A. Hydrocarbon
B. Absorption base
C. Paraffin
D. Hydrocarbon and Paraffin
4. Paraffin are main constituent of
A. Absorption bases
B. Water soluble bases
C. Emulsion bases
D. Oleaginous bases
5. Bees wax is an ingredient of
A. Absorption bases
B. Water soluble bases
C. Emulsion bases
D. Oleaginous bases
6. Polyethylene glycol is the main ingredient of
A. Absorption bases
B. Water soluble bases
C. Emulsion bases
D. Oleaginous bases
7. Polyethylene glycol is known as
A. Paraffin
B. Carbowaxes
C. Anhydrous lanolin
D. Lanolin
8. Titanium dioxide is commonly present in
A. Vanishing cream
B. Sunscreen cream
C. Aqueous calamine cream
D. Ophthalmic cream
9. Which of the following is not a vegetable oil
A. Peanut oil
B. Almond oil
C. Olive oil
D. Petrolatum
10. Which of the following is not a semisolid dosage form
A. Pastes
B. Creams
C. Ointments
D. Suspensions
11. There are ……….types of incompatibility
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
12. Liquefaction is a type of
A. Physical incompatibility
B. Chemical incompatibility
C. Therapeutic incompatibility
D. Chemical & Therapeutic incompatibility
13. Precipitation is a type of
A. Physical incompatibility
B. Chemical incompatibility
C. Therapeutic incompatibility
D. Chemical & Therapeutic incompatibility
14. Alkaloidal incompatibility is a type of
A. Physical incompatibility
B. Chemical incompatibility
C. Therapeutic incompatibility
D. Chemical & Therapeutic incompatibility
15. Error in dosage is a type of
A. Physical incompatibility
B. Chemical incompatibility
C. Therapeutic incompatibility
D. Chemical & Therapeutic incompatibility
16. Which of the following is therapeutic incompatibility
A. Drug interaction
B. Alkaloidal salts with alkaline substances
C. Alkaloidal salts with soluble iodides
D. Precipitation
17. Which of the following is physical incompatibility
A. Drug interaction
B. Alkaloidal salts with alkaline substances
C. Alkaloidal salts with soluble iodides
D. Precipitation
18. Vaginal suppositories are commonly used to treat gynecological ailments, including vaginal infections such as
A. Defecation
B. Acidosis
C. Candidiasis
D. Flatulance
19. Vaginal suppositories are also called as
A. Pessaries
B. Simple suppositories
C. Bougies
D. Rectal suppositories
20. Which of the following method is simple and oldest method of preparation of suppositories
A. Hand molding
B. Compression molding
C. Pour molding
D. Cold compression molding
21. Suppositories are generally evaluated by
A. Melting range test
B. Breaking test
C. Liquefaction
D. Melting range test, Breaking test & Liquefaction
22. Which of the following are suppository bases
A. Fatty bases
B. Water soluble bases
C. Emulsifying bases
D. Fatty bases, Water soluble bases and Emulsifying bases
23. Glycero-gelatin bases are…………..type of suppository bases
A. Fatty bases
B. Water soluble bases
C. Emulsifying bases
D. Emulsifying & Fatty bases
24. Theobroma oil is…………..type of suppository bases
A. Fatty bases
B. Water soluble bases
C. Emulsifying bases
D. Emulsifying & Fatty bases
25. Polyethylene glycols are known as
A. Carbowaxes
B. Polyglycols
C. Macrogols
D. Carbowaxes or Polyglycols or Macrogols
26. Brownian movement of particle in suspension cause
A. Assist sedimentation
B. Promote sedimentation
C. Prevent sedimentation
D. Increase sedimentation rate
27. Which of the following emulsion phenomena is usually reversible?
A. Breaking
B. Coalescent
C. Cracking
D. Creaming
28. Which of the following is the test for identification of emulsion?
A. Dilution test
B. Dye test
C. Conductivity test
D. Dilution test, Dye test & Conductivity test
29. Which of the following is the method for preparation of emulsion?
A. Dry gum method
B. Wet gum method
C. Bottle method
D. Dry gum, Wet gum and Bottle method
30. Which of the following is a volatile oil
A. Castor oil
B. Peppermint oil
C. Almond oil
D. Arachis oil
31. Ideal phase volume ration per stable emulsion is
A. 25:75
B. 50:50
C. 75:25
D. 33:66
32. Events that are likely to occur sequentially in physical unstability are
A. Flocculation, creaming, breaking and coalescence
B. Flocculation, creaming, coalescence and breaking
C. Breaking, coalescence, flocculation and creaming
D. Coalescence. flocculation, creaming and breaking
33. Creaming is a ………..process
A. Reversible
B. Irreversible
C. Reversible & Irreversible
D. Difficult to predict
34. Emulsion made with tweens are
A. w/o
B. o/w
C. Clear
D. Unstable
35. Which of the following would not be described as a colloid
A. Smoke
B. Fog
C. Foam
D. Saltwater
36. The scattering of light by coarse and colloidal dispersed system is known as
A. Contrast matching
B. DLVO theory
C. Tyndall effect
D. Creaming
37. Suspension of hydrophobic drug is formulated with
A. Emulsifying agents
B. Wetting agents
C. Suspending agents
D. Emulsifying & Suspending agents
38. Colloid can
A. Scatter light
B. Not scatter light
C. Adsorb light
D. Evolve light
39. Wetting ability of vehicle is detected by observing
A. Angle of repose
B. Contact angle
C. Critical angle
D. Angle of repose and critical angle
40. Syrup contains
A. 40 % Glycerol
B. 5-40 % Alcohol
C. 66.7 % Sucrose
D. 50 % Sucrose
41. Mandl’s paint is also known as
A. Compound iodine paint
B. Aqueous Iodine solution
C. Strong Iodine solution
D. Lugol’s solution
42. According to USP the concentration of syrup is?
A. 60.7 %w/v
B. 75 % w/w
C. 66.7 %w/w
D. 85 % w/v
43. The most common criteria used to determine the correct pediatric dose of drug is
A. Age
B. Weight
C. Gender
D. Body surface area
44. Prescription is a
A. Dietary chart to patient
B. Diagnosis report to patient
C. A written order from a registered medical practitioner
D. Description of patient symptoms
45. Following are the parts of prescription except
A. Superscription
B. Inscription
C. Subscription
D. Signa
46. Subscription in a prescription is the part of
A. Direction of the pharmacist for preparing the prescription
B. Doctor information
C. Body of prescription
D. Represented by the symbol of
47. Direction to the pharmacist for making medicine is indicated by?
A. Inscription
B. Subscription
C. Superscription
D. Signatura
48. Which is not the part of handling of prescription?
A. Reading
B. Revision of prescription
C. Collecting materials
D. Compounding
49. Pediatric dose calculation on the basis of body weight is calculated using
A. Young’s rule
B. Dilling’s rule
C. Clark’s rule
D. Young’s &Dilling’s rule
50. Using Young’s Rule, calculate the dose for a 5 year old child if the adult dose is 340 mg.
A. 100 mg
B. 200 mg
C. 400 mg
D. 800 mg