Glass containers:
• Glass is the preferred material for containers for injectable products.
• It is principally composed of silicon dioxide tetrahedron which is modified using oxides like sodium, potassium, calcium etc.
Types of glass:
- Type1: Highly resistant borosilicate glass
- Type2: Treated soda lime glass
- Type3: Soda lime glass
- Type4: General purpose glass
• Generally type1 glass is used for most of the sterile products.
• But type 2 and Type 3 glass can also be used when product has non aqueous vehicle.
• The protection of light sensitive drugs can be done by use of amber colored glass which is achieved by iron oxides.
• But iron oxides leach out in the product hence amber colored container should not be used in case of product which has iron catalyzed chemical.
• The glass should have sufficient mechanical strength to withstand high pressure during autoclaving and abuse during processing.
Sterile products made by glass:
Ampules:
• These are single dose containing formulations.
• Generally Type 1 glass is used.

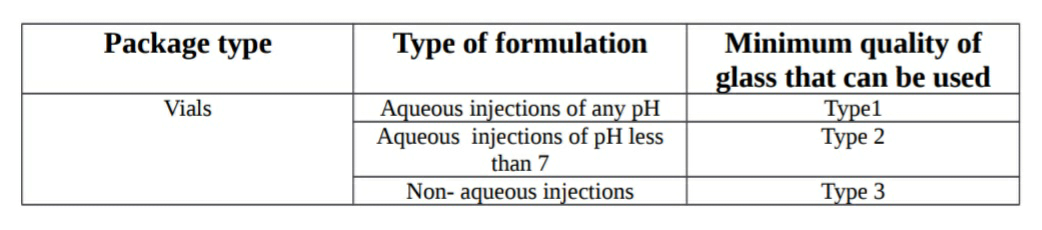
Vials:
These are used for multi dose parenteral products and provided with closure followed by aluminum seal to ensure the air tight packing.
Plastic containers:
Advantages:
• Light in weight
• Non breakable
• Has low toxicity
• Low reactivity with products
Disadvantages:
• Tissue toxicity can occur
• Reactivity due to sorption
• Leaching
Plastic is of two types:
Thermoplastic :
- Polyethylene
- LDPE (Low density polyethylene)
- HDPE (High density polyethylene)
- Polypropylene
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Polystyrene
- Polyamide (Nylon)
- Thermosets:
- Melamine
- Phenol formaldehyde
- Urea formaldehyde
• The two plastics have more interest in parenteral field that is polypropylene and copolymer polyethylene and polypropylene.
• Polypropylene is mostly used plastic because it has high tensile strength, high melting point (165°c) and low permeability to gases and water vapors.

Rubber:
• Rubber closures are mostly used to seal the opening of cartridges, vials, bottles and to provide soft and elastic permit to enter and withdrawn of a needle without loss of integrity of container.
• Principle unit of rubber closure is latex and vulcanizing agent, accelerator, activator, filler etc are added.
• Closures should be non- reactive with the product.
• Physical properties of rubber are elasticity, hardness, porosity.
• Sometimes plastic or lacquer coating is also done to rubber to prevent the sorption, vapor transfer and to provide complete barrier as desired.
