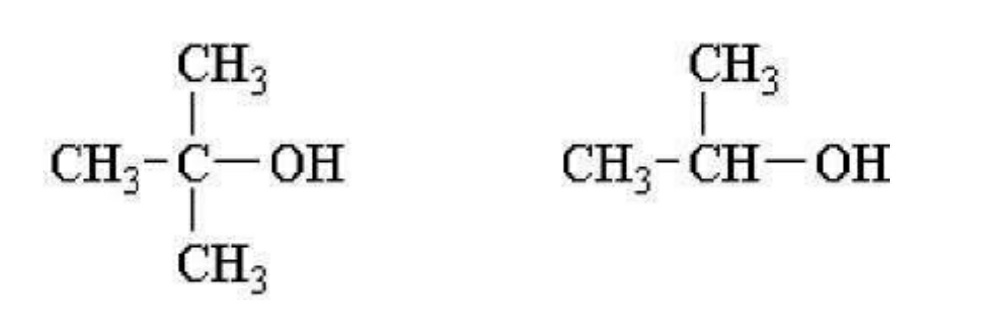PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
1. Which out of the following is NOT a homogeneous mixture?
A) Air
B) Solution of salt in water
C) Solution of sugar in water
D) Smoke
2. Phenol−water system is a/an
A) Element
B) Compound
C) Homogeneous system
D) Heterogeneous system
3. A molal solution is one that contains 1 mole of a solute in
A) 1000 g of the solvent
B) One litre of the solvent
C) One litre of the solution
D) 22.4 litres of the solution
4. Recently the unit of atomic mass amu is replaced by
A) u
B) mol
C) g
D) kg
5. Which of the following law states that equal volume of all gases contain equal number of molecules?
A) Boyle’s law
B) Charles’ law
C) Avogadro’s law
D) Gay Lussac’s law
6. Which of the following contains more molecules?
A) 1 g CO2
B) 1 g N2
C) 1 g H2
D) 1 g CH4
7. Which of the following NSAIDs is an indol derivative?
a) Ibuprofen
b) Indomethacin
c) Meclofenamic acid
d) Diclofenac
8. Which of the following NSAIDs is a propionic acid derivative?
a) Ibuprofen
b) Indomethacin
c) Metamizole
d) Diclofenac
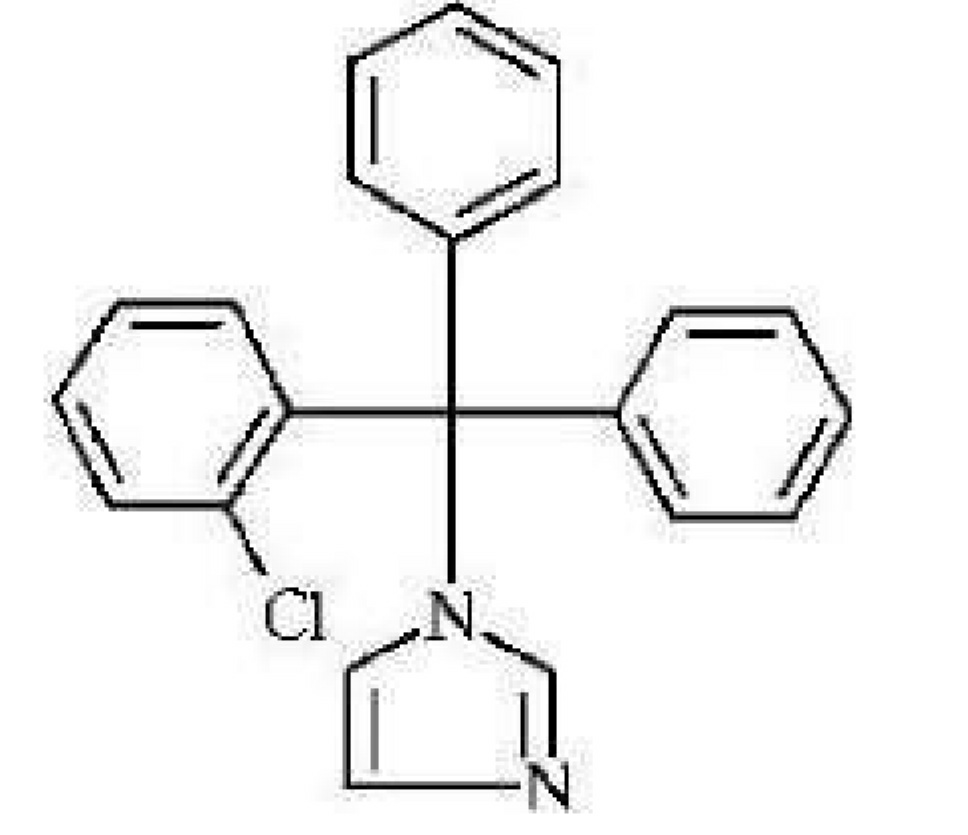
9. Identify the given structure of drug.
a) trimethoprim
b) ketoconazole
c) fluconazole
d) cotrimazole
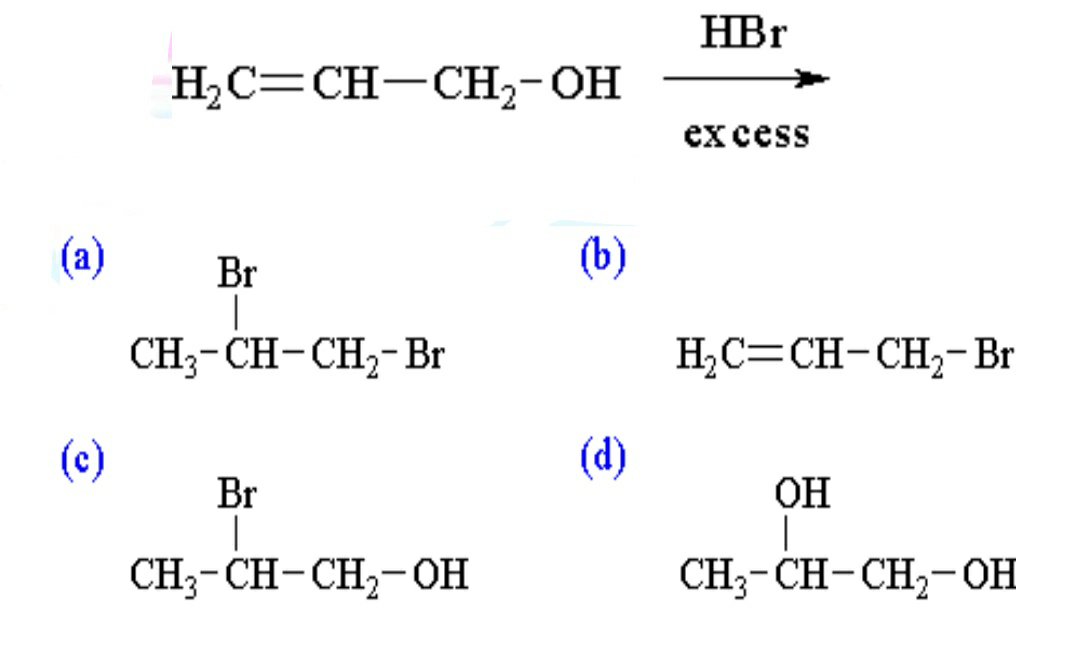
10. What is the major product of the following reaction?
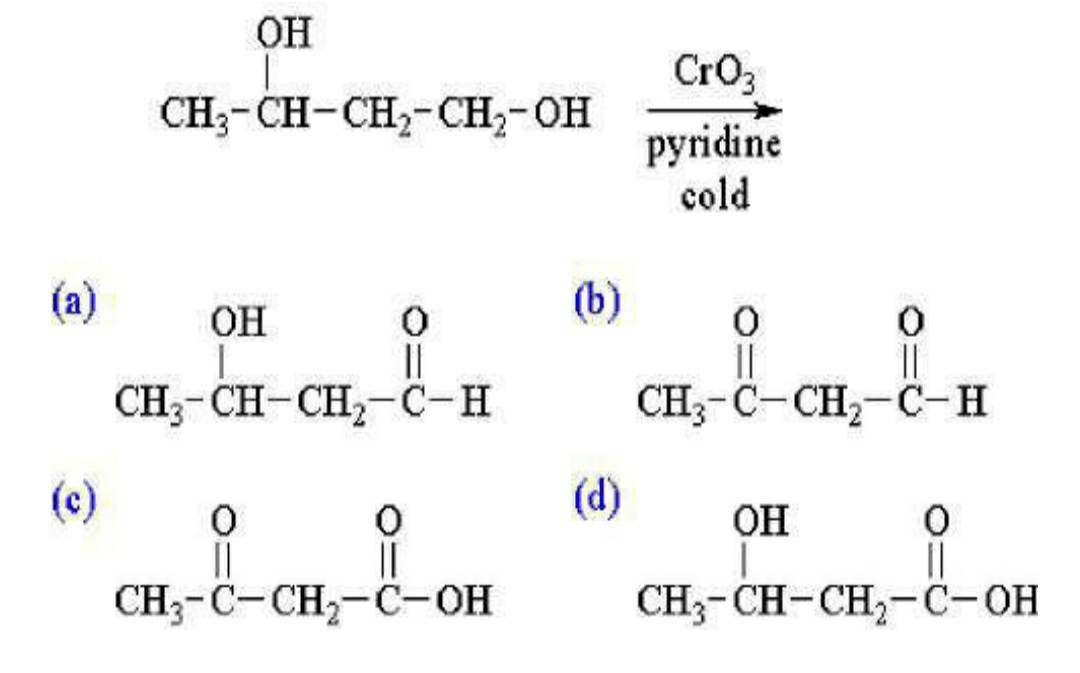
11. What is the major product of the following reaction?
12. Which of the following reagents could be used to distinguish between the following compounds by a visible reaction one that produces either gas bubbles or a color change?
(a) KMnO4, H+, cold
(b) NaOH
(c) CH3MgBr
(d) LiAlH4
13. The major reason that phenol is a better Bronsted acid than cyclohexanol is
(a) it is a better proton donor.
(b) the cyclohexyl group is an electron donating group by induction, which destabilizes the anion formed in the reaction.
(c) phenol is able to stabilize the anion formed in the reaction by resonance.
(d) the phenyl group is an electron withdrawing group by induction, which stabilizes the anion formed in the reaction.
14. The reason that CH3NH2 is a stronger base than CH3OH is due to the fact that…
(a) hyperconjugation resonance of the product, CH3NH3 +, is better than for CH3OH2 +.
(b) resonance of the product, CH3NH3 +, is better than for CH3OH2 +.
(c) the electronegativity of nitrogen is less than oxygen, thus making the electron pair more available.
(d) It isn’t. The oxygen atom has 2 nonbonded pairs of electrons making it twice as basic.
15. 6% solution of urea is isotonic with
(A) 6% solution of Glucose
(B) 25% solution of Glucose
(C) 1 M solution of Glucose
(D) 0.05 M solution of Glucose
16. Which of the following gives an aldehyde on dry distillation?
(A) Calcium acetate + calcium benzoate
(B) Calcium formate + calcium acetate
(C) Calcium benzoate
(D) Calcium acetate
17. A dibromo derivative of an alkane reacts with sodium metal to form an alicyclic hydrocarbon. The derivative is?
(A) 2, 2 – dibromobutane
(B) 1, 1 – dibromopropane
(C) 1, 4 – dibromobutane
(D) 1, 2 – dibromoethane
18. A ligand can also be regarded as
(A) Lewis acid
(B) Bronsted base
(C) Lewis base
(D) Bronsted acid
19. Which cycloalkane has the lowest heat of combustion per CH2 group?
(A) cyclopropane
(B) cyclobutanc
(C) cyclopontane
(D) cyclohexane
20. The ozone layer forms naturally by
(A) the interaction of CFC with oxygen
(B) the interaction of UV radiation with oxygen
(C) the interaction of IR radiation with oxygen
(D) the interaction of oxygen and water vapour
21. Decomposition of benzene diozonium chloride by using Cu2Cl2/HCl to form chlorobenzene is
(A) Cannizarro’s reaction
(B) Kolbe’s reaction
(C) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(D) Raschig’s reaction
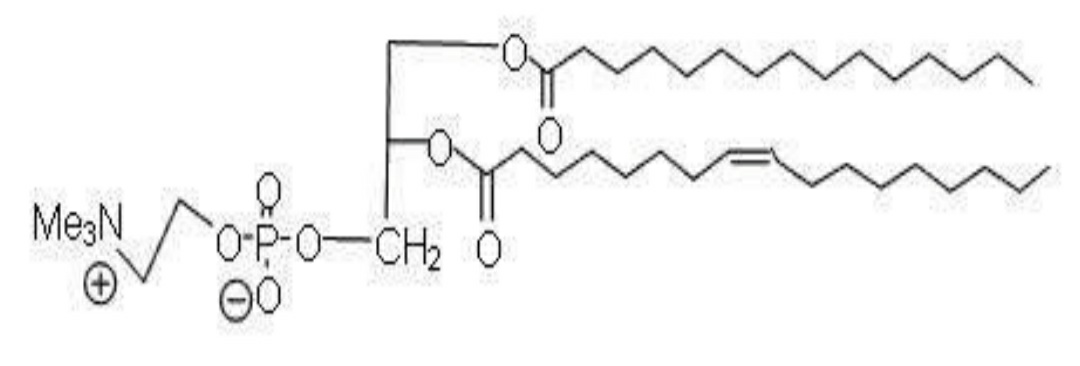
22. What type of molecule is the following structure?
A) A protein
B) A nucleic acid
C) A Phospholipid
D) A carbohydrate
23. Vitamin D2 is :
(a) 22,23-Dihydro -5,6 cis –ergocalciferol
(b) 5,6 cis- chlorcalciferol
(c) 7- dehydrocholesterol
(d) 21,24 – dihydro 5,6 cis ergocalciferol
24. The raw material for synthesis of propranolol is
(a) α – Napthylamine
(b) β naphthol
(c) α naphthol
(d) 1- nepthaldehyde
25. 2- amino -5-chorbenzophenone is the convenient starting material for the synthesis of
(a) Nitrazepam
(b) Diazepam
(c) Choramphenicol
(d) Trimethoprim
26. Pregnenolone, an intermediate in synthesis of steroids, on oppeneur oxidation gives
(a) Progesterone
(b) 9α – flurocortisone
(c) Triamcinolone
(d) α methyl Prednisolone
27. Carbamazepine is tricyclic antidepressant, It is classified as
(a) Benzodiazepine
(b) Arylalkonolamine
(c) Iminostilbene
(d) Benzimidazole
28. Testosterone can be commercially synthesis from
(a) Sarsapogenin
(b) Mexogenin
(c) Oubagenin
(d) Halotensin
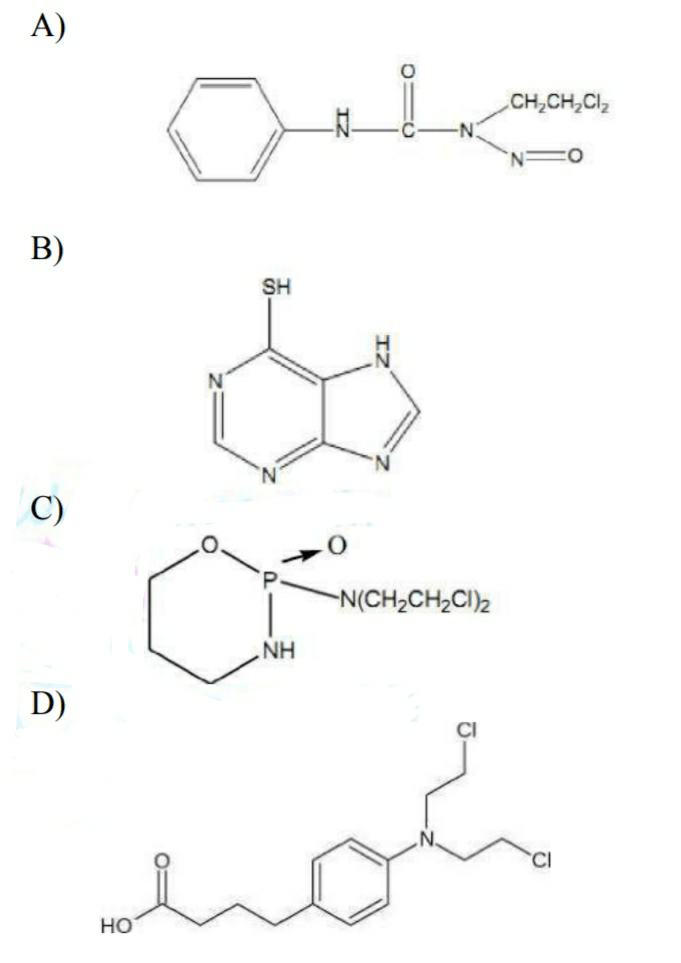
29. Chlormbucil is an anticancer drug. Its structure is?
30. Prazepam differ in structure from diazepam by
(a) N- methyl group
(b) N –cyclopropyl group
(c) N-cyclopropyl methyl group
(d) N-propyl group
31. Betamethasone is:
(a) 9 α Fluro 11 ß , 17 α, 21 trihydroxy 16 ß methyl pregna-1, 4 diene 3, 20 dione
(b) 9 α Fluro 12 ß , 13 α, 21 trihydroxy 17 ß methyl pregna-1, 4 diene 3, 20 dione
(c) 9 α Fluro 11 ß , 17 α, 21 trihydroxy 16 ß methyl estra-1, 4 diene 3, 20 dione
(d) 9 α Fluro 11 ß , 17 α, dihydroxy 16 ß methyl pregna-1, 4 diene 3, 20 dione
32. In phenonthiazine tranquillizing agents, replacement of C-2 hydrogen by chlorine
(a) decreases activity
(b) increases activity
(c) activity unaffected
(d) leads to decreased penetration into the CNS
33. IUPAC nomenclature of the sulindac analogue is:
(a) (Z)-5-Fluoro-2-methyl-1- phenylmethylene-1H-indene-3-acetic acid
(b) (E)-5-Fluoro-2-methyl-1- phenylmethylene-1H-indene-3-acetic acid
(c) 5-Fluoro-2-methyl-1-phenylmethylene- 1H-indene-3-acetic acid
(d) (R)-5-Fluoro-2-methyl-1- phenylmethylene-1H-indene-3-acetic acid
34. Cocaine is monoacid tertiary base which on treatment with hot dilute acids gives?
(a) ecogonine, methyl alcohol & scopic acid
(b) ecogonine, methyl alcohol & cinnamic acid
(c) ecogonine, methyl alcohol & benzoic acid
(d) ecogonine, ethyl alcohol and benzoic acid
35. Triamcinolone is
(a) 9 α -Fluoro-16 α-hydroxyprednisolone
(b) 9 ß -Fluoro-16 α -hydroxyprednisolone
(c) 9 α -Fluoro-16 ß -hydroxyprednisolone
(d) 9 α -Bromo-16 α -hydroxyprednisolone
36. The active metabolite of anti-cancer cyclophosphamide is:
(a) N – hydroxyl cyclophosphamide
(b) N – methyl cyclophosphamide
(c) 4 – hydroxyl cyclophosphamide
(d) N – acetyl cyclophosphamide
37. Beta-Carboline ring system present in
(a) Emetine alkaloid
(b) Cortisone acetate
(c) Deserpidine molecule
(d) Atropine alkaloid
38. According to Pauli exclusion principle, spins of two electrons in same orbital are?
(a) parallel to one another
(b) perpendicular to one another
(c) opposite to one another
(d) supporting one another
39. Benzathine penicillin is
(a) an equimolecular composition of Amoxicillin + N.N dibenzyl ethylene diamine
(b) a molecular complexation of Benzyl penicillin+ N.N dibenzyl ethylene diamine
(c) a molecular complexation of Cloxacillin + ethylene diamine
(d) equimolecular proportion of Amoxicillin + ethylene diamine
40. The Anticancer alkylating drug, a derivative of chloroethylamine
a) Methotrexate
b) Cisplatin
c) Cyclophosphamide
d) Carmustine
41. Tick the anticancer alkylating drug, a derivative of ethylenimine
a) Mercaptopurine
b) Thiotepa
c) Chlorambucil
d) Procarbazine
42. Anticancer drug, a pyrimidine antagonist
a) Fluorouracil
b) Mercaptopurine
c) Thioguanine
d) Methotrexate
43. All of the following drugs are derivatives of nitrosoureas, EXCEPT?
a) Carmustine
b) Vincristine
c) Lomustine
d) Semustine
44. Folic acid contains
A) pteridine ring
B) glutamic acid
C) p -aminobenzoic acid
D) all of above
45. At which carbon tetracycline
undergoes epimerization?
A) C-4
B) C-3
C) C-2
D) C-5
46. Basic ring of vitamin A is
A) α-ionone
B) chromane
C) β-ionone
D) coumarin
47. All __vitamins are isoprenoid compound.
A water soluble
B fat soluble
C both
D none
48.Ring present in thiamine is?
A) Pyrimidine
B) Thiazole
C) a & b
D) Pyridine
49. Sulphur containing monocarboxylic acid?
A Biotin
B Pantothenic acid
C Choline
D Cobalamine
50. Which ring is present in vitamin B12?
A Corrin
B Ionone
C Chromane
D Thiophene