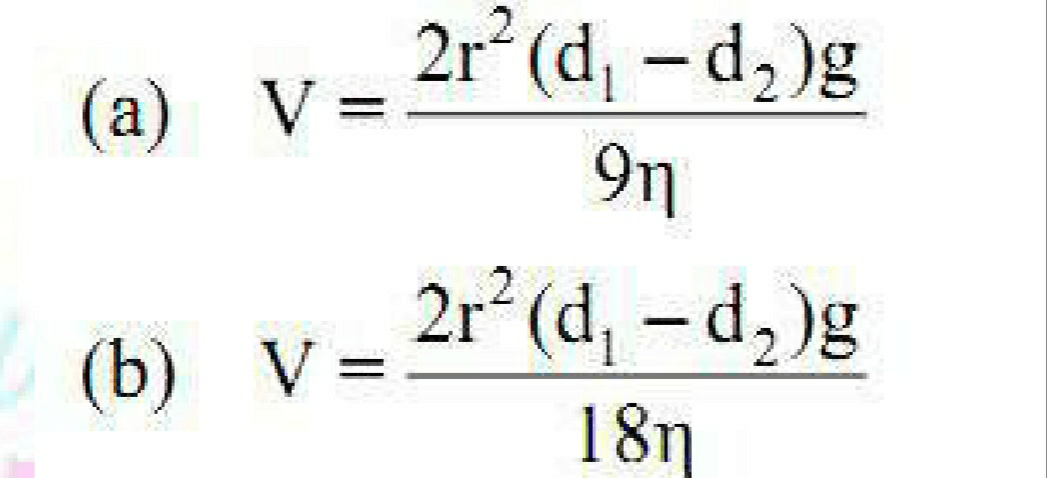PHARMACEUTICS
1. The ability of a substance dissolves in a given solvent system is depends on
(a) Nature and intensity of the forces present in the solute
(b) Nature and intensity of the forces present in the solvent
(c) Interactions between solute and solvent
(d) All the above
2. Which of the following substances having poor water solubility
(a) Weak electrolytes
(b) Non-polar molecules
(c) Both
(d) None
3. The solubility of weak electrolytes & non-polar substances can be increased by adding water miscible solvents. This process is known as
(a) Co-solvency
(b) Complexation
(c) Both
(d) None
4. How co-solvents increase the solubility of poorly soluble drugs?
(a) By reducing the interfacial tension between the predominant aqueous solution and hydro-phobic solute
(b) By reducing the interfacial tension between solute and solvent
(c) Both
(d) None
5. Which of these co – solvents are used to increase the solubility of a drug
(a) Ethanol
(b) Sorbitol
(c) Glycerin
(d) All the above
6. Which of these co – solvent is accepted as a co – solvent in parenteral products, but its use in oral liquids is limited
(a) Glycerol formal
(b) Glycerol
(c) Dimethyl acetamide
(d) None
7. Due to which factor, dimethyl acetamide is not been used as a co-solvent in oral liquids
(a) Due to objectionable odor
(b) Due to objectionable taste
(c) Both
(d) None
8. Thiomersal is belongs to which category preservative
(a) Acidic
(b) Neutral
(c) Mercurial
(d) Quaternary ammonium compounds
9. Which of the following are widely used and excellent preservatives
(a) Mercurial
(b) Quaternary ammonium compounds
(c) Both
(d) Acidic
10. Benzalkonium chloride is categorized as
(a) Acidic preservative
(b) Neutral preservative
(c) Mercurial preservative
(d) Quaternary ammonium compounds
11. At which concentration, phenol act as preservative
(a) 0.2 – 0.5%
(b) 0.5 – 0.8%
(c) 0.05 – 0.1%
(d) None
12. Which of the following sugar has bitter taste
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Saccharine
(d) None
13. Which of the following is a synthetic sweetener
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Sorbitol
(d) Aspartame
14. To increase the viscosity of liquid, which of the following agents are used
(a) PVP
(b) Methyl Cellulose
(c) Sodium Carboxy Methyl Cellulose
(d) All the above
15. Which of the following agents are used as flavoring agents
(a) Menthol
(b) Chloroform
(c) Both
(d) None
16. Most widely used flavoring agent in food industry
(a) Menthol
(b) Chloroform
(c) Mono sodium glutamate
(d) None
17. Which of the following flavor is not responsible for sour taste
(a) Citrus flavors
(b) Liquorice
(c) Raspberry
(d) Mint spice
18. The filling method of a pharmaceutical liquid depends on the following factors
(a) Viscosity of the liquid
(b) Surface tension of the liquid
(c) Compatibility with the materials used in the construction of the filling machine
(d) All the above
19. Which of the following methods are generally used in liquid filling
(a) Gravimetric
(b) Volumetric
(c) Constant level method
(d) All the above
20. In the formulation of suspensions, generally which types of drugs are selected?
(a) Hydrophilic (b) Hydrophobic
(c) Both (d) None
21. In the formulation, to facilitate the wetting of insoluble solids, which of the following agents used
(a) Suspending agents
(b) Flavoring agents
(c) Wetting agents
(d) None
22. How surfactants will facilitate or aid wetting of hydrophobic materials in liquid
(a) By decreasing the solid-liquid interfacial tension
(b) By increasing the solid-liquid interfacial tension
(c) Both
(d) None
23. Stoke’s equation is expressed as
(c) Both
(d) None
24. The stability of suspensions can be evaluated by
(a) Sedimentation volume
(b) Degree of flocculation
(c) Re-dispersibility
(d) All
25. To identify the emulsion type, which of the following tests are conducted?
(a) Dilution test
(b) Dye test
(c) Conductivity test
(d) All
26. The temperature at which the inversion occurs depends on emulsifier concentration is known as
(a) Phage temperature
(b) Inversion temperature
(c) Phase inversion temperature
(d) All
27. Which of the following mechanical equipment can be used for emulsification?
(a) Homogenizers
(b) Mechanical stirrers
(c) Ultra sonifiers
(d) All
28. Which of the following is not used as an emulsifying agent?
(a) Surfactant
(b) Hydrophilic colloids
(c) Electrolytes
(d) Finely divided solids
29. HLB system was developed by
(a) Griffin
(b) Stock’s
(c) Dalla Valle
(d) None
30. Gum Arabic is a
(a) Anionic polysaccharide
(b) Cationic polysaccharide
(c) Neutral polysaccharide
(d) None
31. Which of the following is not a Semi solid dosage form
(a) Paste
(b) Creams
(c) Ointments
(d) Suspensions
32. Generally pastes contain
(a) High percentage of insoluble solids
(b) Low percentage of insoluble solids
(c) Both
(d) None
33. Most widely used hydrocarbon in Semi-solid dosage forms
(a) Petrolatum
(b) Mineral oil
(c) Both
(d) None
34. Which of the following hydrocarbon waxes are employed in the manufacture of creams and ointments?
(a) Paraffin wax
(b) Ceresin
(c) Both
(d) None
35. Which of the following is not a vegetable oil
(a) Peanut oil
(b) Almond oil
(c) Olive oil
(d) Petrolatum
36. Which of the following fatty acid used in water removable creams as emulsifier
(a) Stearic acid
(b) Palmitic acid
(c) Both
(d) None
37. Combination of a surfactant with oilsoluble auxiliary emulsifier is known as
(a) Simple emulsifier system
(b) Mixed emulsifier system
(c) Both
(d) None
38. Promulgen means
(a) Anionic emulsifiers composed of fatty alcohols & their ethoxylates
(b) Non-ionic emulsifiers com-posed of fatty alcohols & their ethoxylates
(c) Cationic emulsifiers composed of fatty alcohols & their ethoxylates
(d) All the above
39. Promulgen D contains
(a) Cetyl alcohol & Ceteareth-20
(b) Stearyl alcohol & Ceteareth-20
(c) Both
(d) None
40. Promulgen G contains
(a) Cetyl alcohol & Ceteareth-20
(b) Stearyl alcohol & Ceteareth-20
(c) Both
(d) None
41. With promulgen D, which type of emulsion generally obtained?
(a) Liquid emulsion
(b) Thick consistency emulsion
(c) Both
(d) None
42. With promulgen G, which type of emulsion generally obtained?
(a) Liquid emulsion
(b) Thick consistency emulsion
(c) Both
(d) None
43. Which of the following polyols used as humectants in creams
(a) Glycerine
(b) Propylene glycol
(c) Sorbitol 70%
(d) All the above
44. The choice of humectants is based on
(a) Rate of moisture exchange
(b) Viscosity and texture of preparation
(c) Both
(d) None
45. Which of the following is more hygroscopic at low concentration?
(a) Sorbitol 70%
(b) Glycerine
(c) Both
(d) None
46. Due to which factors, petrolatum is most widely used as a hydrocarbon basic in ointments
(a) Its consistency
(b) Its neutral characteristics
(c) Its ability to spread easily on the skin
(d) All
47. Water number means
(a) Maximum amount of water that can be added to 100 g of a base at given temperature
(b) Maximum amount of water that can be added to 10 g of a base at given temperature
(c) Maximum amount of water that can be added to 5 g of a base at given temperature
(d) All
48. Lanolin is which type of base
(a) Hydrocarbon base
(b) Absorption base
(c) Both
(d) None
49. In the preparation of vanishing creams, which types of bases are used generally?
(a) Absorption bases
(b) Water removable bases
(c) Hydrocarbon bases
(d) None
50. In the preparation of cold creams, which types of bases are used generally?
(a) Absorption bases
(b) Water removable bases
(c) Hydrocarbon bases
(d) None