PHARMACEUTICAL WAREHOUSING
INTRODUCTION:
• Maintaining proper storage condition for pharmaceutical products and
paramedical is vital to ensure their quality, safety and efficacy.
• Factory stores will invariably be receiving duly approved raw materials and packaging materials from third party.
• A suitable space is provided to raw material, handling of raw & packaging
materials required for manufacturing, including packaging of pharmaceuticals.
This space is known as warehouse.
• It is a part of pharmaceutical company.
PURPOSE:
• To enable the fastest and cheapest transport of drugs and medical equipment from suppliers to beneficiaries.
• There are mainly 3 stages:
✓ Purpose of pharmaceutical products
✓ Storage of ordered products
✓ Distribution of stocked product
VARIOUS AREAS OF WARE HOUSING:
1. RECEIVING AREA:
Includes initial inspection, cleaning and weight checking.
2. SAMPLING AREA
With adequate facilities to prevent cross contamination
3. STORAGE AREA
Including specific storage like air condition rooms, cold rooms, hazardous chemical storage room
4. REJECTED MATERIALS
Destroy or retented unsuitable
5. DISPENSING AREA
With adequate facilities to preclude cross contamination during dispensing
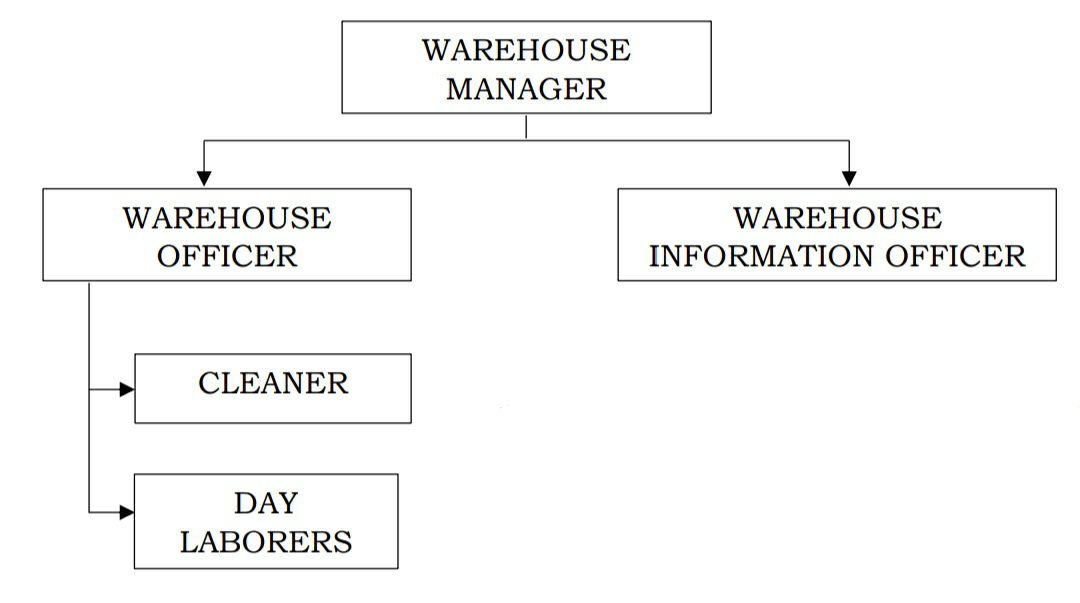
ORGANISATION CHART
DESIGN:
PRINCIPLE: Premises must be located, Designed, constructed, adapted, and maintained to suit the operation to be carried out.
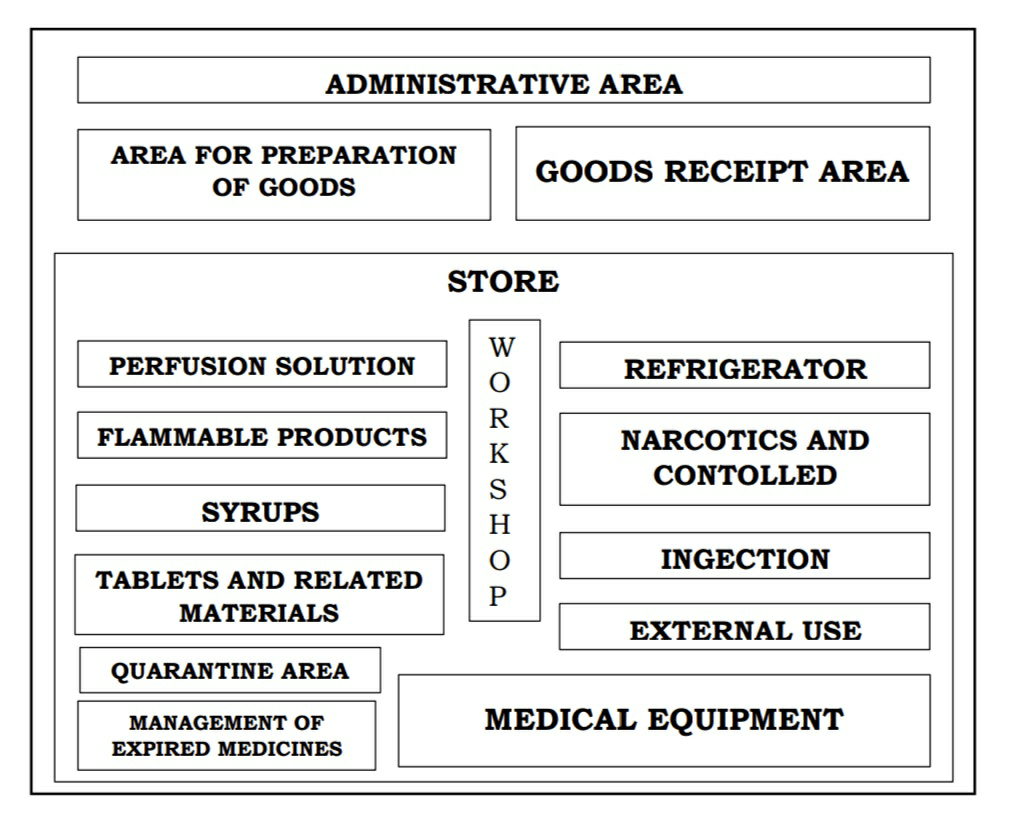
LAYOUT OF THE PHARMACEUTICAL WAREHOUSE
PHARMACEUTICAL WAREHOUSE:
GENERAL:
✓ The layout and design of premises must aim to minimize the risk of errors and permit effective cleaning and maintenance in order to avoid cross-contamination, buildup of dust or dirt, and in general, any adverse effect on the quality of product
✓ Where dust is generated (e.g., during sampling, weighing, mixing and processing operations, packaging of powder) measures should be taken to avoid cross- contamination and facilitate cleaning
✓ Premises should be situated in an environment in which the minimum risk of any contamination of materials or products
✓ Premises used for the manufacture of finished products should be suitably
designed and constructed to facilitate good sanitation
✓ Premises should be careful maintained, and it should be ensured that repair and maintenance operations do not causes any hazards to the quality of products
✓ Premises should be cleaned and where applicable, disinfected according to
detailed written procedures, records should be maintained
✓ Electrical supply, lighting, temperature, humidity and ventilation should be appropriate and such that they do not adversely affect, directly or indirectly, either the pharmaceutical products during their manufacture and storage, or the accurate functioning of equipment
✓ Premises should be designed and equipped so as to afford maximum protection against the entry of insects, birds or other animals. There should be a standard procedure to prevent from rodent and pest control
✓ Premises should be designed to ensure the logical flow of materials and personnel.
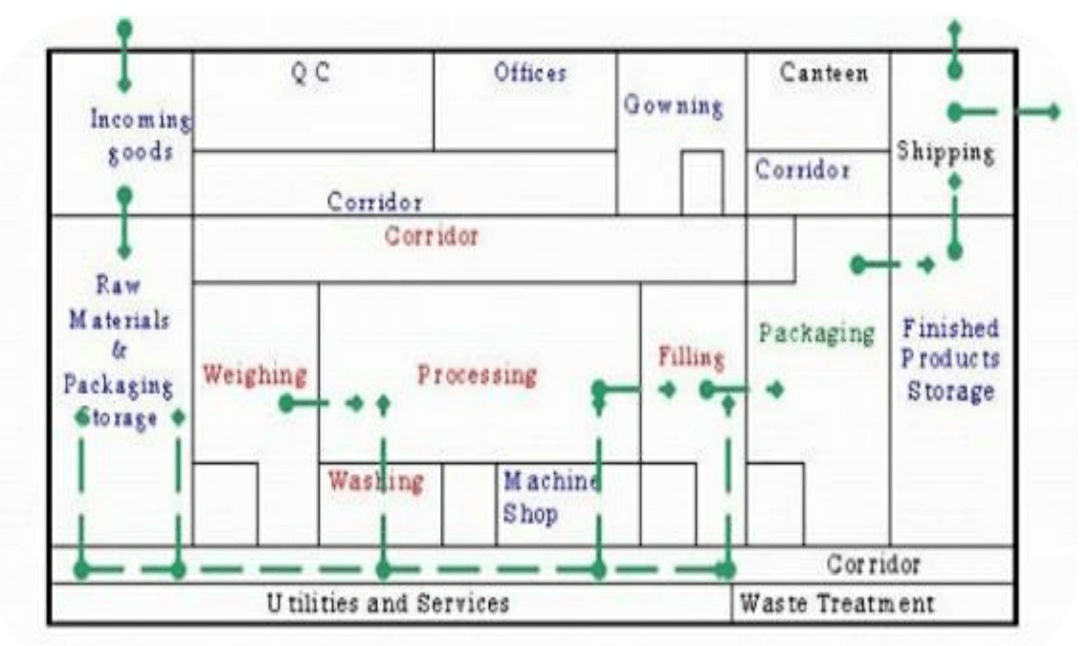
MATERIAL AND PEOPLE FLOW:
Arrival of goods, Entrance for visitors, Entrance for workers, shipment of goods
GENERAL GUIDE LINES:
1. Materials received against specific supply devices
2. Each such consignment have written documents (delivery Chelan)
3. All materials received by responsible persons
4. Materials to be checked for cleanliness and package integrity
5. Damaged container separated and reporting immediately
6. Check for proper container labeling
i.e., status of materials—UNDER TEST,
-A waiting for APPROVAL
GOOD WAREHOUSING PRACTICE:
• Factory stock which should be received with proper documents detailing the
names of product, the batch number, the number of units of final packs of each
batch, the date of dispatch and the quality control status of the batches
• The stock control system must be such that only passed batches of products are issued for distribution. Stocks should be stored, product wise to enable quick identification and control of stock movement. Stocks should therefore be racked and stored in a manner that earlier stocks are more early accessible than the later ones.
• The picking and assembling areas should be so arranged as to minimize the
distance travelled by warehoused operators. Picking stocks should be located on shelves at convenient heights and with proper labels which clearly identify the products
• Assembled products should be checked for accuracy of quantities and identities of products ordered. Batch details should be recorded in relevant documents
• Finished product should be packed in the containers and dispatched for the transportation.
• The unit product packs should be not contaminated by other products. Vehicles which carry the final packaged stocks of products should be so selected that-
1. They are clear, dry and sufficiently protected from rain and other
weather factors
2. They are free from infestation
3. They do not give off strong odors which may contaminate the products.
4. They are suitable to withstand the weight of the load they carry
RULES FOR WAREHOUSING:
1. Systemic storage of the delivered goods.
2. Use air circulation and protection against rodents
3. Keeping a space at least 50cm between the rows of pellets walls.
4. Providing each product have only one specific place.
5. On shelves clear labeling of products should be there
6. Adequate space should be provided for each goods.
7. Provide separate stoke card for each products.
8. All boxes in stock should be closed
9. Flammable products should stored in separate place
CHARACTERS OF GOOD WAREHOUSE:
• Properly cleaned
• Good preservation of drugs and equipments
• Provide safety for staff and stocked goods
• Control of air, light, humidity and temperature
• Products to be purchased according to needs
• Order the destruction of unsuitable products
• Promote rational use of pharmaceutical products
THE WARE HOUSE STAFFS:
1. The responsible pharmacist and his duties
▪ Goods management of the stock of the warehouse
▪ Good preservation of drugs and equipments
▪ Safety of stored goods
2. The warehouse keeper and his duties
▪ Reception of supplies
▪ Storage of stocks of goods
▪ Recording of every IN and OUT movement of the product in the stock card.
▪ Issue of products during manufacturing.
3. The warehouse workers and his duties
▪ Handling operations includes the carrying and moving of goods which are
intended for storage, shipment and sale
▪ The warehouse staffs helps in receives and issue goods and maintain
inventory
4. The cleaner and his duties
▪ Ensure cleanliness of premises and equipment
5. The security guard and his duties
▪ He is responsible for ensuring supervision and security of the warehouse.
STORAGE OF RAW AND PACKAGING MATERIALS:
• Storage conditions- special storage area with controlled temperature, humidity and stored off from the floor
✓ Bottles, vials, ampoules, tins, tubes should be stored in a manner that they
do not contaminated by extraneous matter
✓ Printed packaging material also stored properly
✓ Printed materials such as labels, printed films/foils/laminates, cartons
should kept in storage cupboards
✓ Preventing mix up of printed and non-printed materials
✓ Physical segregation of printed and labeled containers should be made
✓ Special precautions is needed for the storage of-packaging labelling
controlled products
✓ Appropriate storage condition to be provided
HANDLING & ISSUE- RAW MATERIALS:
• Attention to be made for – prevent cross contamination, health of personnel
handling materials, containers should be closed properly, materials that support microbial growth are handled carefully. e.g. agar
• Materials issued only against authorized person
• Personnel protective devices like gloves, facemasks, etc. should be used to avoid health hazards. Adequate dust extraction system should be provided to such away fine dust as to prevent cross-contamination.
✓ Packaging materials issued to production only against packaging materials order
✓ Care should made to check for only right packaging materials to be issued
✓ Unlike raw materials, exact quantity of packaging materials to be issued
✓ Unused packaging materials returned to the warehouse & will accompanied
by authorized documents.
WAREHOUSING OF FINISHED PRODUCTS:
• For avoiding deterioration, spoilage or breakage
• Requirements:
✓ Safe, orderly and dispatch of all products-cold storage area have temperature monitoring and recording devices-racking and shelving system should have good mechanical strength
• Procedures:
✓ Stock received from factory with proper documentation (name, batch
number, date of dispatch)
✓ Finished products which are- under test “must be quarantined and
segregated from-passed stocks”
✓ Stock should be stored product wise to enable quick identification and
controlled stock movement
✓ Stock rotation should be on- first in, first out basis.
WARE HOUSING OF RETURNED GOODS:
• Stocks should be carry out only consultation with quality controlled manager
• Returned goods must be isolated on receipt, clearly identified and records
regarding reason for the return
• QC manager should examine whether these goods are reprocessed or destroyed
• Reprocessing of returned should be done according the instruction of QC manager
SANITATION:
• Written sanitation programs should be available. Including cleaning procedure for
premises and equipment, a quality standard for water, instruction for hygiene
when manufacturing and handling goods, and instruction related to health,
hygienic practices, and clothing of personnel and the disposal procedure for waste
materials and unusable residues
• Eating, smoking, and unhygienic practices should not be permitted in
manufacturing area
• There shall be written procedures for use of suitable rodenticides, insecticides,
fungicides, fumengating agents and cleaning and sanitizing agents.
• Cleaning procedure should be followed, including equipment and materials
MAINTANACE:
• Any building used in manufacture, processing, packing, or holding of drug
product shall be maintained in a good state of repair
• Deterioration of building not only presents a poor image of facility, it can also impact on product quality
• Cracks and holes in walls, floors, or ceilings can provides access for inserts, birds, dirt or microorganisms
• They can also hinder cleaning and sanitation, thereby increasing potential for cross contamination or microbial multiplication
• Floor cracks can also because a safety hazard for people or even dislodge materials from trucks.
• The ingress of water from roof leaks can cause significant damage to materials and equipment, give raise to electrical failures and fires and results in damage to basic structure of the building
• Additionally, holes in the roof or near the top buildings provide ready access to
birds, which may then be encouraged to nest within the building.
RECORDS:
Following records should be in place:
• Receiving goods
• Issuing goods
• Training
• Monitoring temperature and humidity
• Cleaning operation
• Pest control
• Calibration
• Preventative maintenance
• Recall
• Complaints
• Inventory
• Log of signature
STOCK MANAGEMENT:
OBJECTIVES:
• To ensure continuity of supplies
• To avoid over stocking
ISSUING OF MATERIALS:
• Store should issue raw and packing materials on the basis of FCFO (First Come First Out) basis. Entry and exit of every consignment of materials should entered on the stock card
• While issuing hazardous and explosive materials, the operation should be
supervised to prevent any mistakes.
QUALITY ASSURANCE (SOPs):
• Each warehouses will have to establish operating procedures
• They must be clearly defined for each stage activities
• Direct purchase from raw materials manufactures
• Purchase via Head quarters
• Reception of local and imported orders
• Unpacking, labeling, and storage of products
• Computerized stock managements
• Preparations of an orders for delivery
• Returns of drugs
• Managements of expired drugs
• Safety and cleanliness of premises.