CALIBERATION AND VALIDATION
INTRODUCTION
• Analytical instruments are used for a specific analysis of drugs and pharmaceuticals.
• So, regular performance verification are made to ensure that the instruments used in the analytical purpose should be properly validated and calibrated “to
demonstrate that it is suitable for its intended purpose”.
DEFINITION
1. Calibration
• Calibration is a process which ensures that an instrument or measuring
devices producing accurate results.
• Which are compared to the standard results.
• e.g. weigh balance, pH meter.
2. Validation
• It is a integral part of quality Assurance.
• Validation is a process of confirming that the instrument is installed correctly,
that it is operating effectively, and that it is performing without error in documental evidence.
• It does not compared to standard results.
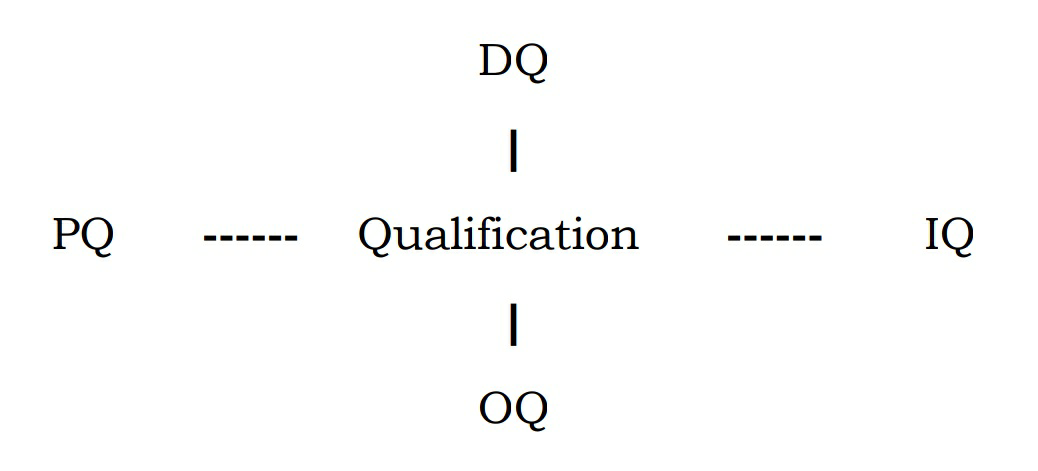
QUALIFICATION
• Qualification is an act or process to assure something complies with some
conditions, standard or specific requirements.
• It is a part of validation.
• It is the action of proving that any equipment or process works correctly and consistently and produces the expected results.
Types:
• Design Qualification
• Performance Qualification
• Installation Qualification
• Operational Qualification
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF CALIBRATION, VALIDATION, QUALIFICATION
CALIBRATION
• Calibration is the activity of checking, by comparison with a standard, the accuracy of a measuring instrument of any type.
• It may also include adjustment of the instrument to bring it into alignment with the standard.
VALIDATION
• The validation of a test method is the process by which the relevance and
reliability of the method are assessed for a particular purpose.
• It is an essential stage in the evolution of the method from its development to its
acceptance and application for regulatory purposes
QUALIFICATION
“It is the action of proving and documenting that equipment or ancillary systems are properly installed, work correctly and actually lead to the expected results. “
IMPORTANCE OF VALIDATION:
• Validation assures a great importance for – Quality Assurance and cost reduction.
• Validation produces product fit for intended use. Quality; Safety and Effectiveness may be designed and built in to product.
• Validation is key element in assuming the quality of the product.
• Parameters controls determined the validation of any process or system.
• It helps to determine the worst case and risks that may arise during the manufacturing of the quality products.
• Validation helps to investigate the deviations caused during the process.
• Deep study and understanding of the system and equipment are made possible due to the validation.
• The risk of the regulatory non-compliance is minimized after the validation.
• A validated process required less process control and the finished product testing.
• Batch to batch variation is minimized due to the validation of processes, systems and equipment.
• Reduces the production cost of the product.
• Increases the production of manufacturing facility due to the minimized rework and rejection.
• Decreases the chances of the failure of the batches.
• Assurance of quality
✓ Time bound
✓ Process optimization
✓ Reduction of quality cost.
✓ Minimal batch failures, improved efficiently and productivity.
✓ Reduction in rejections
✓ Increased output
✓ Fewer complaints about process related failures.
✓ Reduced testing in process and in finished goods.
✓ More rapid and reliable start-up of new equipment’s
✓ Easier maintenance of equipment
✓ Improved employee awareness of processes.
✓ More rapid automation.
✓ Government regulation (Compliance with validation requirements is necessary for obtaining approval to manufacture and to introduce new products)
SCOPE OF VALIDATION:
• A written report on the outcome to be produced.
• Validation over a period of time, e.g. at least three consecutive batches (full
production scale) ta demonstrate consistency.
• Process, materials and equipment to prove consistent yield of a product of the required quality.
• Manufacturers to identify what validation work is needed
• Significant changes (facilities, equipment, processes) should be validated
• Risk assessment approach used to determine the scope and extent of validation – needed.
• Analytical Test Methods
• Instrument Calibrations
• Process Utility Services
• Raw Material
• Equipment
• Facilities
• Product Design
• Cleaning
TYPES OF VALIDATION
VALIDATION :
• Validation means rectification or confirmation
• Validation can be defined as a procedure that demonstrates that a process under standard conditions is capable of consistently producing a product that meets the established product specifications.
Types of Validation
The major types of Validation
• Process validation
• Cleaning validation
• Equipment validation
• Analytical method validation
PROCESS VALIDATION
As per FDA Nov.2008,
‘The collection of data from the process design stage throughout production, which establishes scientific evidence that a process is capable of consistently delivering quality products’
Types of Process validation:
• Prospective Validation.
• Retrospective Validation.
• Concurrent Validation.
• Revalidation.
CLEANING VALIDATION
• Cleaning validation ensures that there is no cross contamination in a multi- product manufacturing plant and also prevents microbial contamination.
• Once a product is manufactured, the equipment is cleaned using appropriate
establish cleaning SOP’S established during IQ of the equipment
Types of contamination to be considered in cleaning validation
• Cross contamination
• Microbial contamination
• Contamination by cleaning or sanitizing agent
• Contamination by other agents
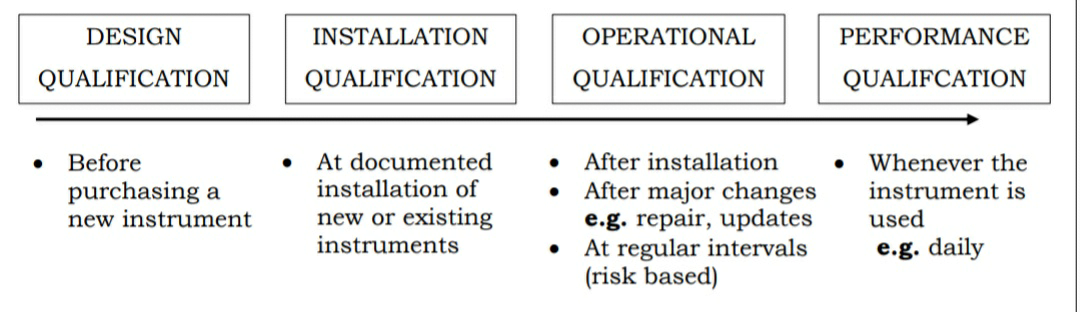
EQUIPMENT VALIDATION
As per FDA. May 1987,
• Action of proving that any equipment works correctly and leads to the expected result is equipment qualification.
• It is not a single step activity but instead result from many discrete activities.
Steps involved..
User requirement specification
1. Design qualification
2. Installation qualifications
3. Operational qualifications
4. Performance qualification
ANALYTICAL METHOD VALIDATION
• Method validation is the process used to confirm that the analytical procedure employed for a specific test is suitable for its intended use.
TYPES OF PROCEDURES TO BE VALIDATED
1. Accuracy
2. Precision
3. Repeatability
4. Reproducibility
5. Specificity
6. Linearity
7. Intermediate precision
8. Qualification limit
9. Quantitation limit
10.Robustness
11.Ruggedness
ACCURACY
The accuracy of analytical method refers to the closeness ement between the observed value and the value whether is either vonti a true one or reference one.
PRECISON
The precision of an analytical method refers to the closeness of vales obtained from a series of vests.
REPEATABILITY
Repeatability is established when the same sample is estimated repeatedly by the same analyst using same analytical method within the same laboratory using same instrument and performed with in a short period of time.
LIMIT OF DETECTION
The lowest amount of analyte in a sample that can be detected but not necessarily quantitated, under the stated experimental conditions.
RUGGEDNESS
The degree of reproducibility of test results obtained by the analysis of the same sample under a variety of conditions such as different laboratories, different analysts, different instruments, different lots of reagents, different elapsed assay times, different assay temperatures, different days, etc.”