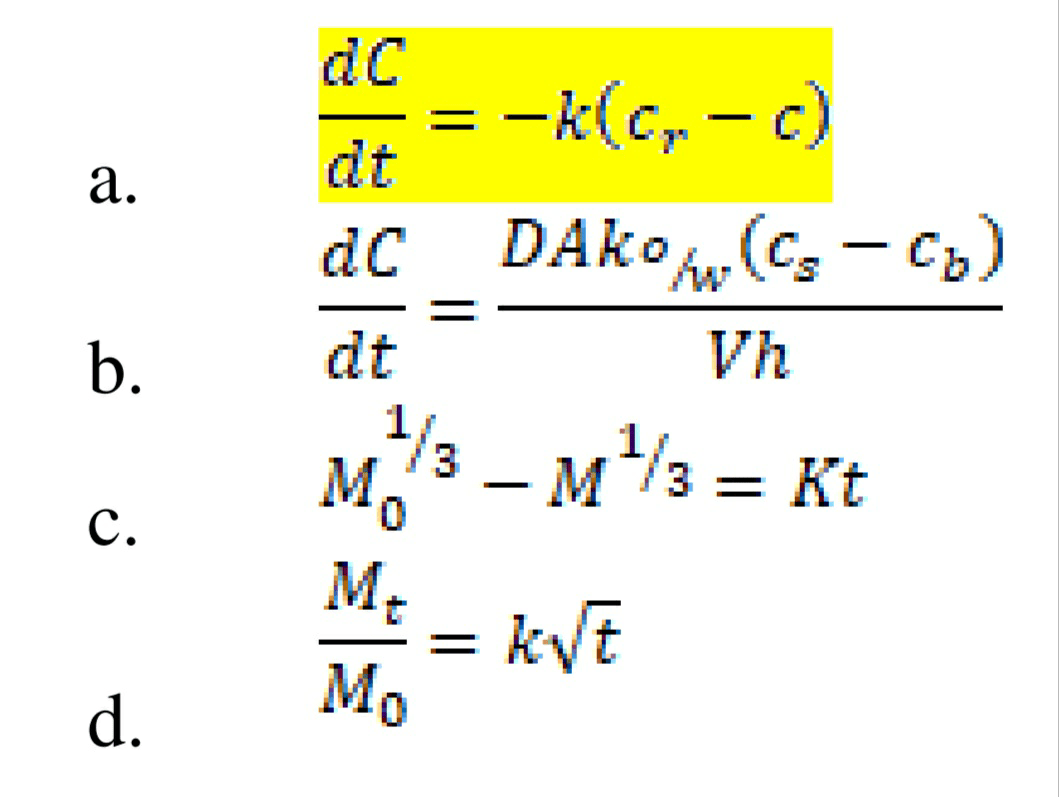1. A spherical solid lipid particle prepared from physiological lipid, dispersed in water or in aqueous surfactant solution.
A. Solid lipid nanoparticle
B. Liposome
C. Niosome
D. Nanoparticle
2. A prominent structure for ocular absorption of drugs
A. Conjunctiva
B. Choroid
C. Sclera
D. Cornea
3. The polymer used in “Lacriset”
A. Hydoxy ethyl cellulose
B. Hydoxy Methyl cellulose
C. Methyl cellulose
D. Hydroxy propyl cellulose
4.An ocular device that has the shape of a flag
A. Ocusert
B. Lacrisert
C. NODS
D. SODI
5. Which of the following does not constitute an appendageal route?
A. Sweat glands
B. Hair follicle
C. Sebaceous gland
D. Stratum corneum
6. “Transderm-Scop” is used in the treatment of
A. Hypertension
B. Angina
C. Motion sickness
D. Antidote for smoking
7. The size of particles in a a parenteral suspension should be
A. 10 to 20 µm
B. Less than 10 µm
C 100 to 200 µm
D.50 to 100 µm
8. The anterior part of the nasal cavity opening towards the face.
A. Nasopharynx
B. Nasal septum
C. Nasal vestibule
D. Nasal turbinate
9. Monolithic devices
A. have drugs with large therapeutic indices
B. have rapid drug permeation
C. only hydrophilic polymers are used
D. release is through a polymer membrane
10. Drug release from osmotic drug delivery systems depends on
A. osmotic pressure
B. ionic strength
C. osmotic pressure & ionic strength
D. osmotic pressure & environment in git
11. One method to prepare nanoparticles is
A. pan coating
B. filtration
C. solubilisation
D. precipitation
12. Excipient to increase density of GRDDS is
A. zinc oxide
B. talc
C. sodium bicarbonate
D. calcium carbonate
13. __________ is a dispersed matrix system
A. nanospheres
B. nanoparticles
C. nanocapsules
D. nanopolymers
14. Chitosan is a __________ mucoadhesive polymer
A. cationic
B. anionic
C. synthetic
D. non-ionic
15. Which of the following is a natural polymer used in nanoparticles.
A.Polycaprolactone
B. Polylactic acid
C. Alginate
D. Polystyrene
16. A microcapsule has____________
A. Drug dispersed in matrix
B. Dug core surrounded by distinct wall
C. Drug adsorbed on the surface
D. Drug distributed in polymeric matrix
17. A polymeric implant that is biodegradable
A. Prepared from silicone
B. Prepared from Polyurethane
C. Prepared from Polylactic acid
D. Prepared from polyacrylate
18. Paracellular route for nasal drug delivery is
A. Slow and passive lipodial pathway
B. Slow and passive aqueous pathway
C. Fast and active aqueous pathway
D. Fast and active lipodial pathway
19. Sodium taurocholate used as penetration enhancer is
A. A Surfactant
B. Fatty acid with surfactant property
C. Bile salt with surfactant property
D. Bile salt but no surfactant property
20. pH of nasal formulation in the physiological range
A. Keeps the drug in ionized state
B. Alters physiological ciliary movements
C. Increases mucosal irritation
D. Keeps the drug in unionized state and sustains physiological ciliary movements
21. Mucocilliary clearance is
A. A barrier to nasal absorption
B. Not a barrier to nasal absorption
C. It is protective in function
D. It is a barrier to nasal absorption but also protective in function
22. Reservoir systems
A. do not depend on area
B. have a rate controlling membrane
C. follow any order of kinetics
D. are highly porous
23. Factors affecting lymphatic uptake include
A. larger aqueous phase
B. greater hydrophilicity of nanoparticles
C. low concentration of surfactant
D. longer chain length of lipid
24. Stealth liposomes
A. have short half-life
B. are taken up by macrophages
C. have very large size
D. are sterically stabilized
25. An example of a polymer incorporated into dendrimers is
A. propylene glycol
B. polyethyleneimine
C. polyurethane
D. styrene copolymers
26. Modified balance method is used to evaluate
A. particle size
B. adhesive strength
C. drug release
D. swelling
27. Eudragit L100 is a type of
A. cellulose polymer
B. vinyl co-polymer
C. methacetic acid co-polymer
D. methacrylic acid co-polymer
28. A Primary Irritation index of <2 for a transdermal patch indicates that patch is
A.Non-irritant
B.Slightly irritant
C.Moderately irritant
D.Severely irritant
29.Ideal glass transition temperature for a pressure sensitive adhesive used in transdermal system should be
A. – 20° C to – 40° C
B. – 2° C to – 4° C
C. 20° C to 40° C
D. 2° C to 4° C
30. Ocusert is an example of
A. Feedback regulated system
B. Activation modulated system
C. Bio -responsive system
D. Membrane permeation system
31. __________ is an advanced method of determining size of nano particles
A. Atomic force microscopy
B. Ultrasound scattering
C. Compound microscopy
D. Molecular microscopy
32. Chimeric peptides have
A. chylomicrons
B. polymeric micelles
C. peptidomimetic antibodies
D. polymeric nanoparticles
33. Use of monoclonal antibodies for drug delivery to tumors is
A. active targeting
B. passive targeting
C. triggered drug targeting
D. vector targeting
34. _____ is an example of a synthetic biodegradable polymer
A. acrolein
B. polyethylene glycol
C. LDPE
D. polystyrene
35. _______is an example of a bioerodible polymer
A. polyorthoesters
B. polycarbonate
C. fluorocarbon
D.polystyrene
36. Which amongst this is a limitation associated with conventional drug delivery systems?
a. Lower effectiveness
b. Ease of manufacturing
c. Decreased side effects
d. Spatial and temporal control
37. Carbopols are:
a. Synthetic vinyl polymers with ionizable carbonyl group
b. Polyoxythylene ethers with carboxy groups
c. Mineral waxes with hydrocarbon content ranging from C35 to C55
d. Polyoxyethylene derivatives of plyoxypropylene
38. Which amongst the following are the smallest liposomes?
a. Large unilamellar vesicles
b. Oligolamellar vesicles
c. Multilamellar vesicles
d. Multivesicular vesicles
39. Which of the following is used as chemical cross-linking agent in preparation of nanoparticles?
a. Glutaraldehyde
b. 2,2, di-methyl propane
c. Lactides and glycolides
d. Poly (acryl) starch
40. What type of protein binding characteristics of a drug are desirable to be formulated into an ocular system?
a. Low
b. Medium
c. High
d. It has no bearing
41. A positive temperature-sensitive hydrogel has —————- critical solution temperature
a. Upper
b. Lower
c. Hybrid
d. Mixed
42. The stratum corneum consists of ——————layers of keratinized cells
a. 10 to 25
b. 0 to 10
c. 25 to 50
d. Above 50
43. Peel adhesion is tested by measuring the force required to pull a single coated tape, applied to a substrate at a ………………° angle
a. 180
b. 360
c. 45
d. 90
44. Which of the following is the Noyes – Whitney equation?
45. Which of the following is an effective barrier for drug?
a. Tight junctions
b. Pinocytes
c. Glucose transporters
d. Protein carriers
46. To prevent the loss of drug that has migrated into the adhesive layer during storage, this is used
a. Release liner
b. Rate controlling membrane
c. Adhesive layer
d. Backing membrane
47. Webels model is used for evaluation of
a.Pulmonary Targeting
b.Nasal Targeting
c. Hepatic Targeting
d. Ocular targeting
48. These noninvasive techniques have been used for drug delivery to brain
a. Nanogels
b. Bradykinin administration
c. Onmaya reservoir
d. Microgel
49. In Pulmonary Drug Delivery the drug absorption is achieved due to
a. High lipophilicity and large surface area
b. Low lipophilicity and small surface area
c. High hydrophilicity and large surface area
d. Low hydrophilicity and Small surface area
50. The dissolution study of colon targeted drugs is carried by
a. Bio Dis III apparatus
b. Beaker Method
c. Flow through cell
d. USP Type I AND II Apparatus
51. These are a unique class of synthetic macromolecules having highly branched, three dimensional, nanoscale architecture with very low polydispersity index and high functionality
a. Dendrimers
b. Neosomes
c. Auasomes
d. Nanoparticles
52. _________ is carrier for Haemoglobin
a. Neosome
b. Nanoparticle
c. Aquasomes
d. Phytosomes
53. Following is the example of invasive brain targeting
a. Osmogens
b. Colloidal carriers
c. Amino acid transporters
d. Neosomes