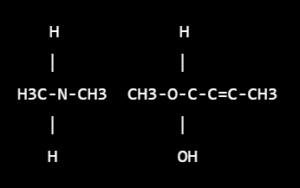
Structure –
I think you may have meant to ask about “salbutamol”, which is also known as “albuterol” in the United States. Salbutamol is a medication used to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The chemical structure of salbutamol can be represented as follows:
- Salbutamol contains a phenylethanolamine backbone with a tert-butyl group and an albuterol moiety at the side chain.
- The albuterol moiety consists of a hydroxyl group and a double bond between the second and third carbon atoms, which contribute to its bronchodilator activity by selectively binding to beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the lungs and promoting relaxation of the smooth muscles surrounding the airways.
The molecular formula of salbutamol is C13H21NO3, and its molecular weight is 239.3 g/mol.
Synthesis –
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol, can be synthesized through a multi-step process from the starting material benzyl cyanide. Here is a brief overview of the synthesis of salbutamol:
- Condensation: Benzyl cyanide is condensed with N,N-dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal (DMF-DMA) to form the imine intermediate.
- Reduction: The imine intermediate is reduced with lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) to form the amine intermediate.
- Protection: The amine intermediate is protected with tert-butyl dimethylsilyl chloride (TBDMS-Cl) to form the corresponding silyl ether.
- Oxidation: The silyl ether intermediate is oxidized with m-chloroperbenzoic acid (MCPBA) to form the corresponding ketone intermediate.
- Reduction: The ketone intermediate is reduced with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to form the alcohol intermediate.
- Deprotection: The silyl ether protecting group is removed with tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF) to yield the final product, salbutamol.
Overall, this synthetic route involves several key steps including condensation, reduction, protection, oxidation, reduction, and deprotection to synthesize salbutamol. The process requires careful control of reaction conditions and purification steps to obtain a high yield and purity of the final product.
SAR( structure-activity relationship)-
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol, is a bronchodilator medication used to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The compound works by selectively binding to beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the lungs, promoting relaxation of the smooth muscles surrounding the airways, and allowing for easier breathing. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) of salbutamol is focused on the chemical features that are necessary for its activity and selectivity at beta-2 adrenergic receptors.
- Phenylethanolamine backbone: The phenylethanolamine backbone of salbutamol is essential for its activity at beta-2 adrenergic receptors, as it allows the compound to interact with the receptor site and promote bronchodilation.
- tert-Butyl group: The tert-butyl group in salbutamol helps to increase the compound’s selectivity for beta-2 adrenergic receptors over other adrenergic receptors, which reduces the risk of side effects.
- Hydroxyl group: The hydroxyl group in salbutamol is critical for its activity, as it allows the compound to form hydrogen bonds with the receptor site and increase its affinity for the beta-2 adrenergic receptor.
- Double bond: The double bond in salbutamol’s albuterol moiety is important for its activity, as it increases the compound’s potency and selectivity for beta-2 adrenergic receptors compared to other adrenergic receptors.
- Stereochemistry: The stereochemistry of salbutamol is also important for its activity, as the R-isomer of salbutamol is more active and selective for beta-2 adrenergic receptors than the S-isomer.
Overall, the SAR of salbutamol highlights the importance of the phenylethanolamine backbone, tert-butyl group, hydroxyl group, double bond, and stereochemistry for its activity and selectivity at beta-2 adrenergic receptors.
Mechanism –
- Salbutamol, also known as albuterol, is a bronchodilator medication used to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The mechanism of action of salbutamol is through its selective binding to beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the lungs, which promotes relaxation of the smooth muscles surrounding the airways and allows for easier breathing.
- When salbutamol is inhaled, it reaches the lungs and binds to the beta-2 adrenergic receptors located on the surface of the smooth muscle cells in the airways. This binding activates a signaling pathway that leads to the relaxation of these muscles, allowing the airways to widen and increase airflow.Salbutanol Salbutanol Salbutanol
- The signaling pathway involves the activation of adenylate cyclase, an enzyme that converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP). cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA), which leads to the phosphorylation of proteins involved in the contraction of smooth muscle cells, causing relaxation of the airway muscles.
- In addition to its bronchodilatory effects, salbutamol also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation in the airways and improve breathing.Salbutanol Salbutanol Salbutanol Salbutanol
- Overall, the mechanism of action of salbutamol involves the selective binding to beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the lungs, leading to the activation of a signaling pathway that promotes the relaxation of smooth muscles and increases airflow.
Uses –
- Salbutamol, also known as albuterol, is a bronchodilator medication that is primarily used to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is also used to prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
- Specifically, salbutamol is used to relieve bronchospasm, which is the narrowing of the airways that occurs in asthma and COPD. It works by relaxing the smooth muscles in the airways, allowing the airways to widen and making it easier to breathe.Salbutanol Salbutanol Salbutanol Salbutanol
- Salbutamol is typically administered through an inhaler or nebulizer, which delivers the medication directly to the lungs. It can also be taken in tablet or syrup form for long-term management of asthma or COPD.
- In addition to its use in respiratory conditions, salbutamol is also used in the treatment of hyperkalemia (high levels of potassium in the blood) and as a tocolytic (to reduce premature labor contractions).
- Overall, salbutamol is a widely used medication for the treatment of asthma, COPD, and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, as well as for other medical conditions such as hyperkalemia and premature labor.